Sound Transmission Class or STC is the rating system by which the ability of a partition to attenuate, (reduce the effect of) airborne sound is measured.
Materials are tested over multiple sound frequencies, from bass levels of 125Hz to treble levels of 4000Hz. They are then assigned STC ratings, a United States standard since 1961.
The partitions tested include:
Both commercial and residential construction rely on these ratings as a way of reducing airborne sound transmission between rooms.
Airborne noise is a result of a person or object making a noise. The noise generates energy in the form of vibrations or sound-waves. These sound waves are picked up by a medium, like air.
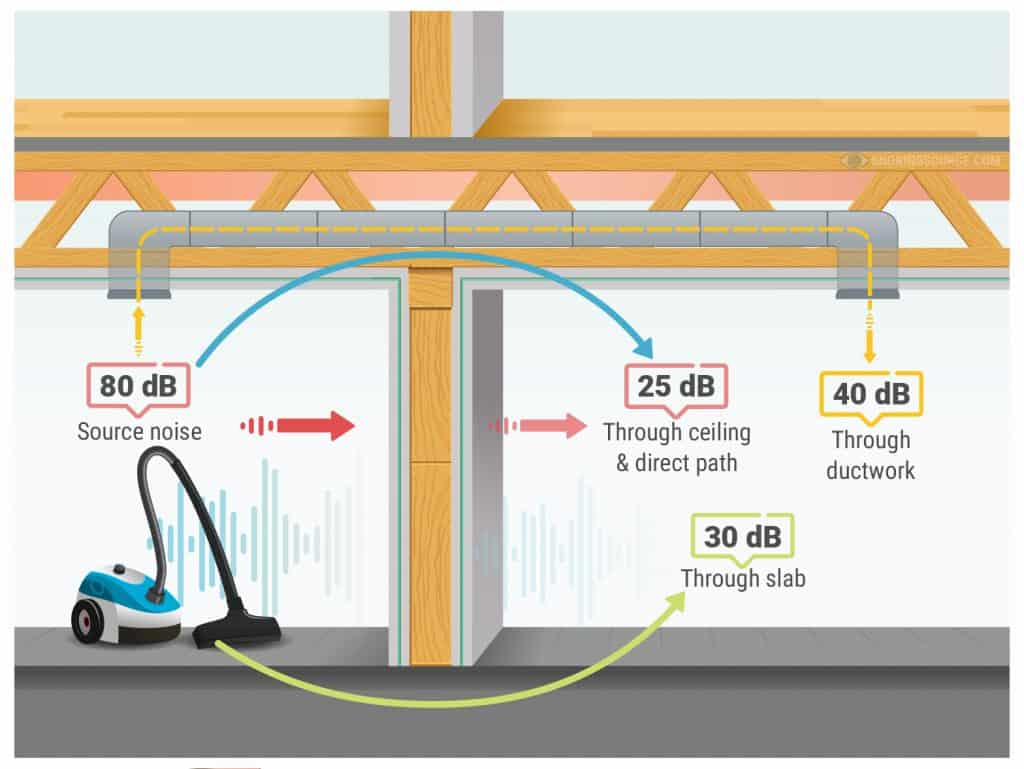
The soundwaves will travel through the air until they collide with a solid object or structure like a wall, ceiling, window, divide, etc. The sound then vibrates and is able to be heard in the adjoining space.
Examples of airborne noise include: people talking, music, and the television.
Basic knowledge of the defining factors of STC ratings allows for a greater understanding of how ratings are achieved and how they relate to soundproofing techniques.
The unit that describes the intensity of sound. Decibel means one-tenth of a Bel and is shown as the abbreviation dB.
The scale is unusual as our ears are exceptionally sensitive and the scale would be inordinate if numbered 1 by 1.
Instead, it relies on a logarithmic scale. Simply shown, near-total silence registers as 0dB and a sound 100 times more powerful is 20dB and 1000 times more powerful is 30dB.
To give this a little perspective;
Frequency is a useful measurement of musical sounds and is expressed in Hertz (Hz).
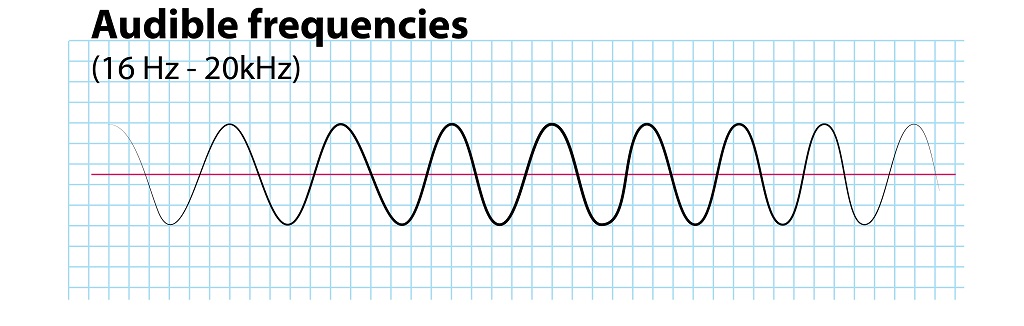
Music has strong repeated sound waves and the speed with which they vibrate determines the pitch of the sound. The number of wave cycles that occur in 1 second denotes the frequency.
Measuring volume from both sides of a dividing wall will give you different results. This is due to sound vibrations decreasing from one side of the wall to the other, the sound waves lose their potency during travel.
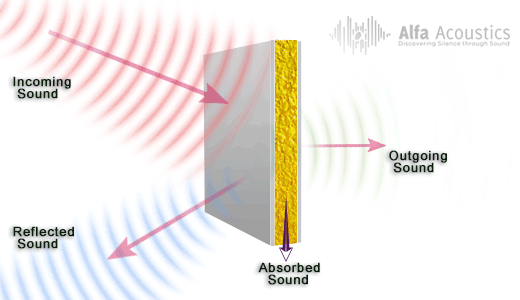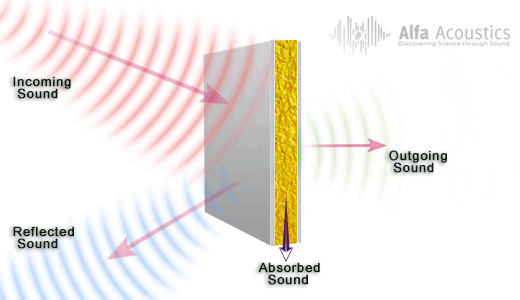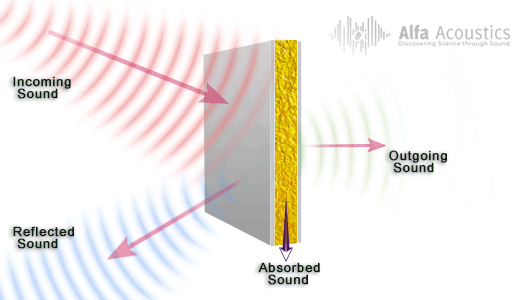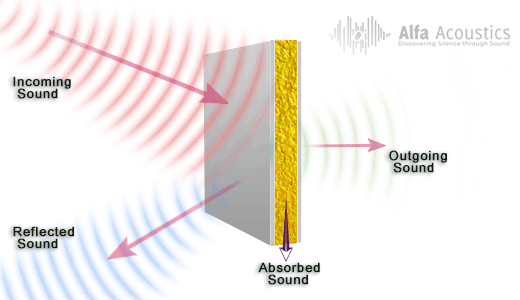
The difference between the two figures is the TL or Transmission Loss coefficient.
For instance:
Loud music on one side of a wall may record 90dB and only 65dB in the neighboring room. Therefore, there is a 25 dB TL.
Frequency of the sound can alter the TL figure greatly, some higher and lower frequencies (pitched) music can have a very similar dB figure with little transmission loss. The sound can be heard almost equally on both sides.
Measuring an STC rating is a complicated process. Multiple differentials are considered, these are called 'deficiencies' when calculating the overall rating.
This is the layman's explanation:
Your curve will be assigned the STC rating from the industry contour that closest resembles yours.
The higher the STC number denotes the greater the ability to reduce sound transmission through a medium.
The necessity for high-quality is contextual, dependent upon what the space will be used for, and how important the blocking of sound transmission is.
For instance, Government buildings, board rooms, and honeymoon suites require an STC rating of 55+. The same applies to multi-unit living, where airborne noise comes from multiple sources and directions.
In some offices and commercial buildings, even small family homes, a mid-range STC rating is sufficient.
As explained above, the scale is sensitive and dramatic differences in sound transmission, and volume might result in a minor rating difference.
The following scale shows the designated STC rating of a full height, internal wall with the conversation taking place on one side, and overheard on the other.
| STC RATING | SOUND |
| 25 | Soft speech can be understood |
| 30 | Normal speech can be understood |
| 35 | Loud speech can be understood |
| 40 | Loud speech is heard, not intelligible |
| 45 | The point where privacy begins |
| 50 | Normal speech can't be heard |
| 55 | Loud speech can't be heard |
| 60 | Very loud speech not audible |
| 65 | Superior soundproofing |
A rough guide when planning noise reduction solutions is as follows:
When assembling thin stud walls, it is a challenge to supply satisfactory soundproofing without taking up too much space.
It might not always be a straight-forward task either, there may be structural and thermal alterations to consider. There is also the aesthetics, adding a layer to a wall means a lot of furniture removal and redecorating.
Adding mass to a wall is the easiest way of improving an STC rating, although this may come at the cost of losing valuable floor space.
Soundproofing is usually thought of after construction. However, the following are some of the best ways to increase the STC rating of a wall during the construction process.
Alternative stud arrangements such as staggered-stud or double-stud construction is an expensive way to raise the rating of an interior wall during construction.
The use of resilient channels are also very effective. The channels are fitted to both wood and metal struts with drywall panels screwed on top.
As long as the installation has been carried out correctly and the drywall is isolated from the struts, noise and vibration have difficulty traveling to the outer wall, resulting in transmission loss.

When looking to increase STC scores to existing walls as a retrofit, resilient channels aren't recommended. There is insufficient space between the wall and the new layer of gypsum for them to be effective.
The addition of fiberboard-based products is cheap and simple. As a stand-alone solution, the boards offer very little in the way of soundproofing, however, when used beneath a layer of drywall, ratings increase by 3 to 5 points.
Metal sound clips work in much the same way as resilient channels, although they can be fitted retrospectively. They rely on a similar method of panel isolation and achieve good STC rating increases. Installation is labor-intensive and is comparatively expensive though.
Overall, the best way to improve STC scores on existing walls is with the addition of single or dual layer of drywall.
Results vary based on multiple factors such as manufacturing process and material used during production and the thickness of each sheet.
It is very important to recognize that STC ratings of mediums cannot simply be added.
James Burkett
To reiterate the above, an STC rating is a logarithmic value, similar to equations.
For example, a wall may have an STC rating of 34 and a single sheet of drywall may have a rating of 20.
When combined, you will not achieve an overall rating of 54, instead, you may see an increase in STC rating of 2 or 3 points.
When installing drywall to a thin stud wall, ensure all gaps are sealed. The smallest gaps of just an inch can result in huge TL loss, as much as 20 STC points.
Some examples of STC improvements of a thin stud wall using sheets of drywall:
Although STC ratings are a solid guide of a material's soundproofing abilities, they shouldn't be solely relied upon.
High-rated walls may still underperform with very low-frequency noise. For sound of 125Hz or below, a more effective soundproofing solution should be employed.
It is a given that people live and work together more harmoniously in quieter environments. Interior walls with low STC ratings are no longer acceptable. Especially when STC ratings in the 50s and 60s are comfortably achievable.
Now the next time you look at a soundproofing material, you'll have a better understanding of what Sound Transmission Class or STC actually means.

Snoringsource.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for website owners to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon(.com, .co.uk, .ca etc) and any other website that may be affiliated with Amazon Service LLC Associates Program.